Understanding Muscle Growth Fundamentals: How To Build Muscle Mass Quickly And Safely At The Gym
How to build muscle mass quickly and safely at the gym – Building muscle mass effectively requires a solid understanding of the physiological processes involved. This section details the key elements contributing to muscle hypertrophy, the increase in muscle size and strength.
Muscle Hypertrophy and Protein Synthesis
Muscle growth, or hypertrophy, is primarily driven by the process of protein synthesis. This is the body’s way of building and repairing muscle tissue. When you lift weights, you create microscopic tears in your muscle fibers. Your body then responds by synthesizing new proteins to repair and rebuild these fibers, resulting in increased muscle size and strength. The rate of protein synthesis is significantly influenced by factors such as training intensity, nutrition, and rest.
Progressive Overload for Muscle Growth
Progressive overload is the cornerstone of any effective muscle-building program. It involves consistently increasing the demands placed on your muscles over time. This can be achieved by gradually increasing the weight, reps, sets, or the difficulty of your exercises. Without progressive overload, your muscles adapt to the stimulus and stop growing. This principle ensures continuous muscle growth and adaptation.
Muscle Fiber Types and Their Roles
Skeletal muscle is composed of different types of muscle fibers: Type I (slow-twitch), Type IIa (fast-twitch oxidative), and Type IIx (fast-twitch glycolytic). Type I fibers are more resistant to fatigue and are crucial for endurance activities. Type II fibers generate more force but fatigue more quickly. Both types are essential for muscle growth, with strength training stimulating hypertrophy in both Type I and Type II fibers, albeit to varying degrees.
Designing a Safe and Effective Workout Program
A well-structured workout program is crucial for maximizing muscle growth while minimizing the risk of injury. This section Artikels a sample 12-week program and emphasizes the importance of proper form and technique.
Sample 12-Week Workout Program
This program utilizes a push/pull/legs split, allowing sufficient recovery time for each muscle group. Remember to adjust weights based on your individual strength levels and always prioritize proper form.
| Day | Exercise | Sets | Reps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday (Push) | Bench Press | 3 | 8-12 |
| Monday (Push) | Overhead Press | 3 | 8-12 |
| Tuesday (Pull) | Deadlifts | 1 | 5 |
| Tuesday (Pull) | Bent-Over Rows | 3 | 8-12 |
| Wednesday (Legs) | Squats | 3 | 8-12 |
| Wednesday (Legs) | Leg Press | 3 | 12-15 |
Workout Split Routine: Push/Pull/Legs
- Push Day: Focuses on pushing movements like bench press, overhead press, and shoulder press.
- Pull Day: Focuses on pulling movements like deadlifts, rows, and pull-ups.
- Leg Day: Focuses on leg exercises like squats, leg press, and hamstring curls.
Proper Form and Technique
Maintaining correct form is paramount to prevent injuries and maximize muscle activation. Focus on controlled movements, avoiding momentum, and engaging the target muscles throughout each repetition. If unsure about proper form, consult a qualified fitness professional.
Warm-up and Cool-down Routines
A proper warm-up prepares your body for exercise, increasing blood flow and muscle temperature. A sample warm-up might include 5-10 minutes of light cardio followed by dynamic stretches. A cool-down promotes recovery and reduces muscle soreness. This could involve static stretches held for 20-30 seconds per muscle group.
Nutrition for Muscle Growth
Optimal nutrition is essential for supporting muscle growth and recovery. This section details macronutrient requirements and provides a sample meal plan.
Macronutrient Requirements
For muscle growth, a balanced intake of protein, carbohydrates, and fats is crucial. Protein provides the building blocks for muscle tissue, carbohydrates fuel your workouts, and fats support hormone production and overall health. A common recommendation is to consume 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily.
Sample Meal Plan
| Meal | Food Item | Macronutrient Breakdown (g) | Serving Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with protein powder and berries | Protein: 30, Carbs: 50, Fat: 10 | 1 cup oatmeal, 1 scoop protein powder, ½ cup berries |
| Lunch | Chicken breast with brown rice and vegetables | Protein: 40, Carbs: 60, Fat: 15 | 4 oz chicken, 1 cup rice, 1 cup vegetables |
Hydration and Muscle Recovery
Adequate hydration is crucial for muscle recovery and overall health. Water helps transport nutrients, regulate body temperature, and remove waste products from your muscles. Aim for at least 2-3 liters of water per day.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals can hinder muscle growth. Ensuring adequate intake of vitamins like Vitamin D and minerals like zinc and magnesium is important for optimal muscle function and growth. A balanced diet or supplementation, if needed under professional guidance, can address these deficiencies.
Recovery and Rest
Recovery and rest are just as important as training for muscle growth. This section highlights the significance of sleep, active recovery, and stress management.
Sleep and Muscle Recovery
Sleep is crucial for muscle protein synthesis and recovery. During sleep, your body releases growth hormone, which plays a vital role in muscle repair and growth. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Active Recovery Methods
Active recovery, such as light cardio or stretching, can improve blood flow, reduce muscle soreness, and promote faster recovery. Light activities like walking or swimming can be beneficial.
Stress Management and Muscle Growth
Chronic stress can negatively impact muscle growth by increasing cortisol levels, a hormone that can break down muscle tissue. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga can optimize recovery and growth.
Overtraining and its Consequences
Overtraining occurs when you consistently train without adequate rest and recovery. Symptoms include persistent fatigue, decreased performance, and increased risk of injury. Listen to your body and incorporate rest days into your training schedule to prevent overtraining.
Supplement Considerations
While not essential, supplements can play a supporting role in a well-rounded muscle-building program. This section explores common supplements and their potential benefits and drawbacks.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Common Supplements
Creatine monohydrate is a popular supplement that can increase strength and power output. Protein powder can help meet daily protein requirements. However, it’s important to remember that supplements are not a replacement for a balanced diet and proper training.
Safe and Effective Supplement Incorporation
Always follow the recommended dosage instructions on supplement labels. Start with a lower dose to assess your tolerance and gradually increase it as needed. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any new supplement regimen.
Comparison of Protein Supplements
Whey protein is rapidly digested and ideal for post-workout consumption. Casein protein is digested more slowly and provides sustained protein release. Soy protein is a plant-based alternative. The best choice depends on individual preferences and dietary needs.
Potential Risks Associated with Supplement Use

Some supplements may interact with medications or have potential side effects. It is crucial to research supplements thoroughly and consult with a healthcare professional before using them, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Gym Equipment and Exercise Selection
Choosing the right gym equipment and exercises is vital for effective muscle building. This section focuses on key compound and isolation exercises.
Effective Gym Equipment

Essential equipment includes barbells, dumbbells, weight machines, and resistance bands. These tools allow for a wide range of exercises targeting various muscle groups.
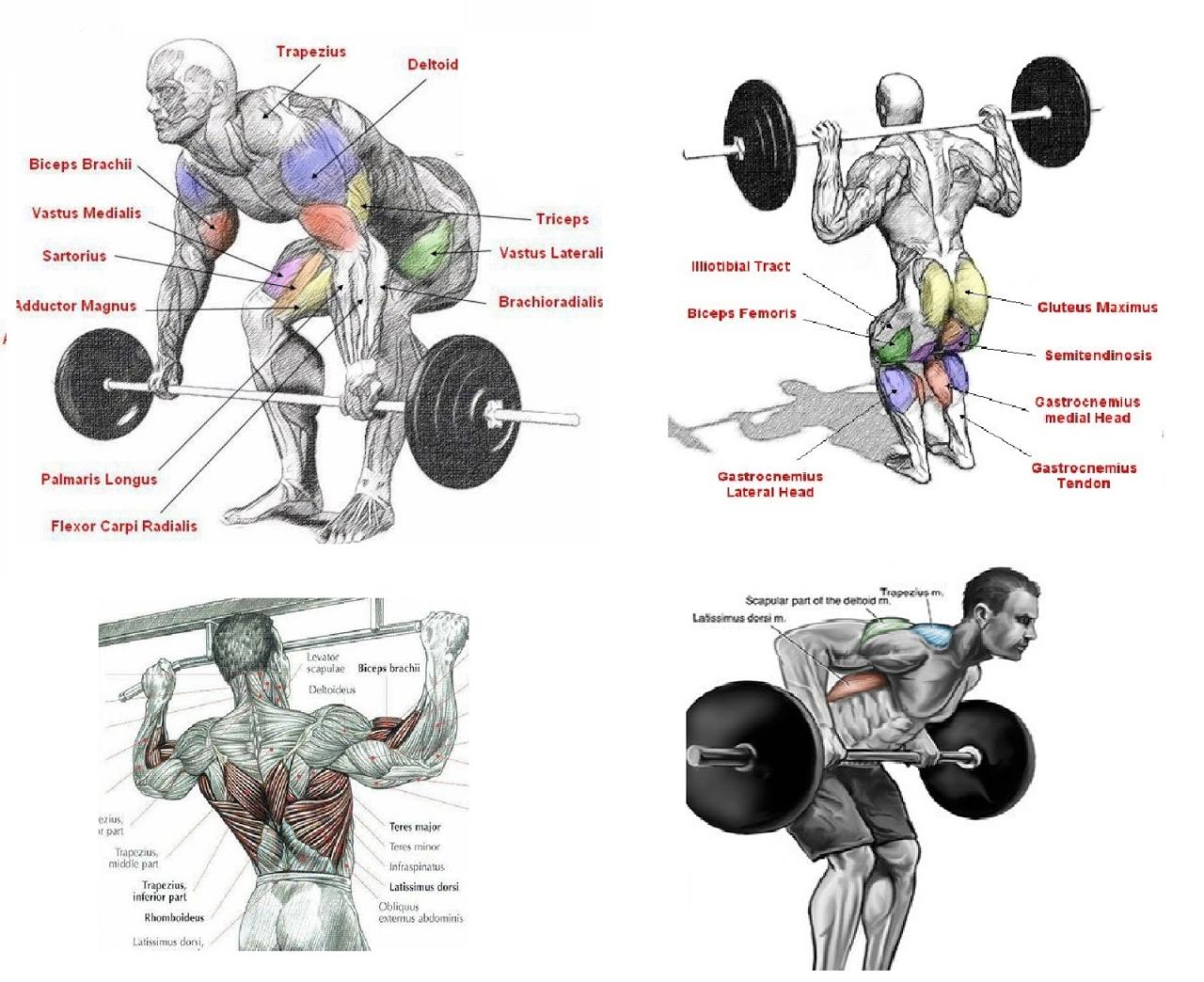
Proper Form for Key Compound Exercises
Squats: Maintain a neutral spine, engage your core, and descend until your thighs are parallel to the ground. Deadlifts: Keep your back straight, maintain a neutral spine, and engage your core throughout the lift. Bench Press: Lie flat on the bench, grip the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width, and lower the bar to your chest. Overhead Press: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, hold the bar at shoulder height, and press it overhead. Rows: Maintain a straight back, pull the bar towards your chest, and squeeze your shoulder blades together.
Variations of Popular Exercises
Many exercises have variations that target muscles slightly differently or allow for adjustments based on individual needs and preferences. Examples include incline bench press, Romanian deadlifts, and different grip variations for rows.
Isolation Exercises
Isolation exercises target specific muscle groups, allowing for more focused hypertrophy. Examples include bicep curls, triceps extensions, and leg extensions.
Monitoring Progress and Making Adjustments
Tracking progress and making adjustments are crucial for continuous improvement and avoiding plateaus. This section discusses methods for monitoring progress and strategies for staying motivated.
Tracking Progress
Methods include tracking weight lifted, body measurements (e.g., chest, waist, arms), and taking progress photographs. These methods provide objective data to assess progress and identify areas for improvement.
Adjusting Training Plans, How to build muscle mass quickly and safely at the gym
If you’re not seeing progress, consider adjusting your training plan. This could involve changing exercises, sets, reps, rest periods, or incorporating different training techniques like periodization.
Listening to Your Body
Pay attention to your body and recognize signs of overtraining or injury. Rest and recovery are essential, and ignoring pain can lead to more serious problems.
Staying Motivated
Staying motivated requires setting realistic goals, tracking your progress, and finding workout partners or joining fitness communities for support and accountability.