Understanding Weight Management
Combining gym workouts with healthy eating habits for weight management – Weight management is a multifaceted process involving a balanced approach to diet and exercise. Effective weight loss or maintenance relies on creating a calorie deficit through a combination of increased energy expenditure (exercise) and reduced caloric intake (diet). Understanding the physiological processes involved in both is crucial for sustainable results.
The Interplay of Exercise and Diet in Weight Loss
Weight loss occurs when the body expends more calories than it consumes. Exercise increases calorie expenditure, while a healthy diet controls caloric intake. The two work synergistically: exercise boosts metabolism and improves body composition, while a balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients to support physical activity and overall health. Without a healthy diet, exercise alone may not yield optimal weight management results.
Physiological Processes of Calorie Burning During Gym Workouts
Gym workouts burn calories through various physiological mechanisms. Cardiovascular exercises like running and cycling primarily utilize aerobic respiration, breaking down carbohydrates and fats to produce energy. Strength training, on the other hand, stimulates muscle protein synthesis and increases resting metabolic rate, leading to higher calorie burn even at rest. The intensity and duration of the workout significantly influence the total calories burned.
Macronutrient Roles in Weight Management
Macronutrients – carbohydrates, proteins, and fats – play distinct roles in weight management. Carbohydrates provide immediate energy, proteins support muscle growth and repair, and fats are essential for hormone production and nutrient absorption. A balanced intake of all three is necessary. The proportion of each macronutrient should be tailored to individual needs and fitness goals, considering factors such as activity level and overall health.
Examples of Healthy Eating Plans for Different Fitness Levels
Dietary plans should be personalized. However, general guidelines can be provided. Beginners might focus on portion control and gradually increasing their intake of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Intermediate individuals can explore more nuanced approaches like calorie cycling or flexible dieting. Advanced individuals may require highly customized plans, possibly involving macro-tracking and adjustments based on performance and recovery.
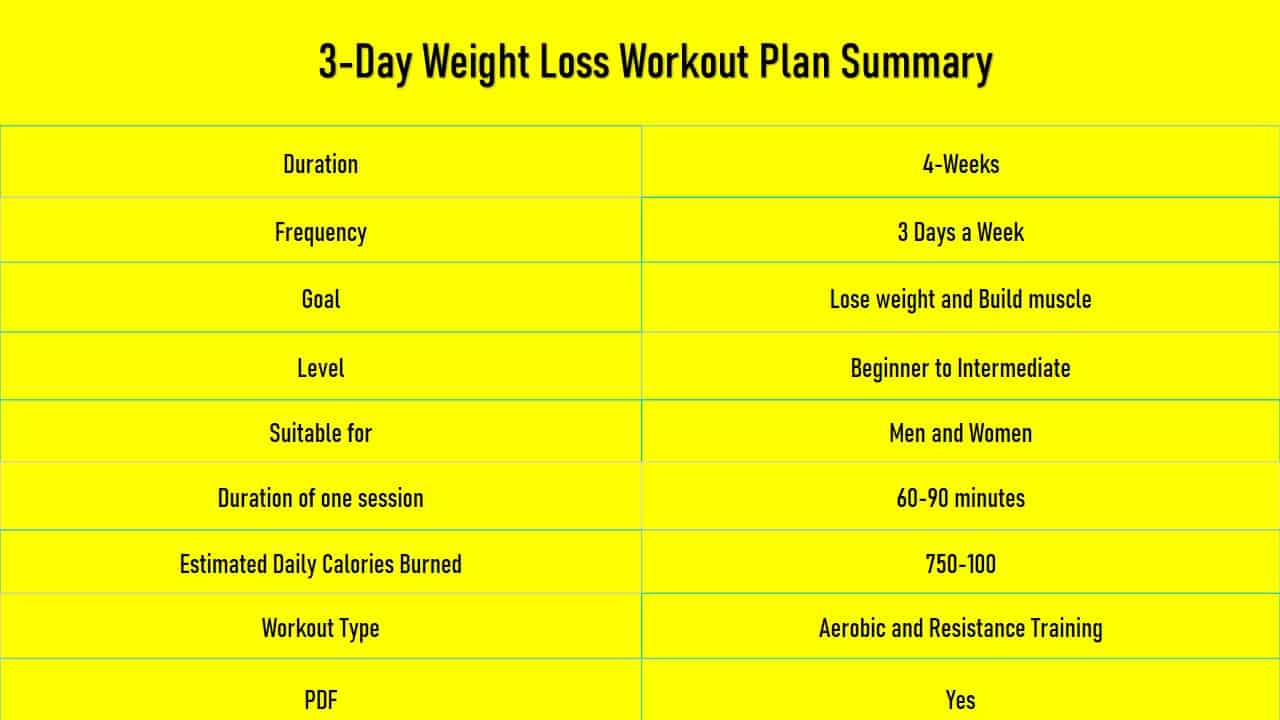
Designing a Workout Plan
A well-structured workout plan is essential for achieving fitness goals and preventing injuries. The plan should be tailored to individual fitness levels, gradually increasing in intensity and volume to promote progressive overload.
Sample Weekly Gym Workout Routine for Beginners
This routine focuses on compound exercises to build a solid foundation of strength and endurance. It incorporates both strength training and cardio, ensuring a balanced approach to fitness.
- Monday: Full-body strength training (squats, push-ups, rows, lunges)
- Tuesday: Cardio (30 minutes of brisk walking or cycling)
- Wednesday: Rest
- Thursday: Full-body strength training (variations of Monday’s exercises)
- Friday: Cardio (30 minutes of swimming or jogging)
- Saturday: Active rest (yoga or light stretching)
- Sunday: Rest
Workout Plan Incorporating HIIT for Intermediate Fitness Levels
HIIT workouts are effective for burning calories and improving cardiovascular fitness. This plan incorporates HIIT sessions alongside strength training for a well-rounded approach.
- Monday: Upper body strength training
- Tuesday: HIIT (20-30 minutes)
- Wednesday: Rest or active recovery
- Thursday: Lower body strength training
- Friday: HIIT (20-30 minutes)
- Saturday: Long, low-intensity cardio (45-60 minutes)
- Sunday: Rest
Workout Schedule Balancing Muscle Building and Cardiovascular Health for Advanced Users
Advanced users can benefit from a more complex schedule that incorporates specialized training techniques and higher volume workouts.
- Monday: Upper body strength training (focus on hypertrophy)
- Tuesday: HIIT and core work
- Wednesday: Lower body strength training (focus on power)
- Thursday: Active recovery (light cardio or mobility work)
- Friday: Full-body strength training (focus on strength)
- Saturday: Long, slow distance cardio
- Sunday: Rest
Importance of Progressive Overload in a Workout Plan
Progressive overload is crucial for continuous improvement. It involves gradually increasing the intensity, volume, or frequency of workouts over time to challenge the body and prevent plateaus. This could involve increasing weight lifted, reps performed, sets completed, or workout duration.
Proper Performance of Common Gym Exercises
Proper form is essential to prevent injuries and maximize results. The following table provides guidance on common exercises:
| Exercise | Muscle Groups Worked | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Squats | Quads, glutes, hamstrings | Maintain proper back posture, avoid rounding the spine. |
| Deadlifts | Entire posterior chain (back, glutes, hamstrings) | Engage core muscles, maintain a neutral spine, avoid rounding the back. |
| Bench Press | Chest, shoulders, triceps | Maintain a stable base, control the weight throughout the movement. |
| Overhead Press | Shoulders, triceps | Engage core muscles, avoid locking out elbows fully. |
Crafting a Healthy Eating Plan: Combining Gym Workouts With Healthy Eating Habits For Weight Management
A healthy eating plan is the cornerstone of effective weight management. It should be balanced, providing all necessary nutrients while controlling caloric intake.
Healthy, Low-Calorie Recipes for Pre- and Post-Workout Meals
Pre-workout meals should provide sustained energy, while post-workout meals aid in muscle recovery and replenishment.
- Pre-workout: Oatmeal with berries and nuts, banana with peanut butter, whole-wheat toast with avocado.
- Post-workout: Greek yogurt with fruit and granola, protein shake with spinach and berries, chicken breast with brown rice and vegetables.
Strategies for Meal Prepping
Meal prepping involves preparing meals or meal components in advance to ensure a consistent and healthy diet throughout the week. This saves time and reduces the likelihood of unhealthy food choices.
- Cook large batches of grains, proteins, and vegetables on the weekend.
- Portion meals into individual containers for easy grab-and-go options.
- Prepare simple snacks like fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
Importance of Hydration and Suitable Beverages
Adequate hydration is crucial for optimal physical performance and overall health. Water is the best choice, but unsweetened tea and infused water are also good options.
Managing Cravings and Avoiding Unhealthy Snacking

Strategies to manage cravings include mindful eating, identifying triggers, and choosing healthy alternatives. This might involve replacing sugary snacks with fruits or vegetables.
Comparison of Different Dietary Approaches for Weight Management
Various diets, such as the Mediterranean diet and the DASH diet, emphasize whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. They differ in their specific macronutrient ratios and emphasis on certain food groups. The best approach depends on individual preferences and health needs.
Integrating Workout and Diet
Sustainable weight management requires a consistent and integrated approach to both exercise and diet. This involves establishing healthy habits and developing strategies to overcome challenges.
Importance of Consistency in Workout Routines and Healthy Eating Habits

Consistency is key. Regular exercise and a balanced diet are more effective than sporadic efforts. Establishing a routine helps to build habits and make healthy choices automatic.
Common Obstacles to Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle and Strategies to Overcome Them
Common obstacles include lack of time, lack of motivation, and social pressures. Strategies to overcome these challenges include setting realistic goals, finding a workout buddy, and seeking support from family and friends.
Role of Sleep and Stress Management in Weight Loss
Sufficient sleep and effective stress management are crucial for overall health and weight management. Lack of sleep and chronic stress can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism.
Sample Daily Schedule Integrating Gym Workouts and Healthy Meals
A sample schedule could involve a morning workout followed by a healthy breakfast, planned lunches and dinners, and mindful snacking throughout the day.
Plan for Tracking Progress and Making Adjustments, Combining gym workouts with healthy eating habits for weight management
Tracking progress through weight measurements, body composition analysis, and fitness assessments helps to monitor effectiveness and make necessary adjustments to the workout and diet plan. Regular self-assessment and feedback are vital.
Visual Aids for Understanding
Visual aids can help illustrate key concepts related to weight management.
Visual Representation of a Balanced Plate
A balanced plate is a visual representation of a healthy meal, typically showing approximately half of the plate filled with fruits and vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with whole grains or complex carbohydrates.
Visual Representation of Calorie Burning During Various Gym Exercises
A bar graph could show the approximate calorie expenditure for different exercises (e.g., running, weightlifting) per unit of time, highlighting the variations based on intensity and duration. The graph would clearly indicate that higher intensity exercises generally burn more calories in a shorter amount of time.
Visual Representation of the Effect of Different Macronutrients on the Body’s Energy Levels
A line graph could illustrate the energy levels throughout the day based on the consumption of different macronutrients. For example, a spike in energy after carbohydrate consumption would be contrasted with a more sustained energy release from protein and fat intake. This visual would emphasize the different metabolic rates and sustained energy release from different macronutrients.


