Zero Carb Protein Powder for Weight Loss
Zero carb protein powder for weight loss – Zero-carb protein powder has emerged as a popular supplement for those seeking effective weight loss. Its appeal lies in its potential to support satiety, muscle preservation, and overall metabolic health within a low-carbohydrate dietary framework. This article delves into the composition, mechanisms, benefits, drawbacks, and practical applications of zero-carb protein powder for weight loss.
Understanding Zero Carb Protein Powder
Zero-carb protein powders are formulated to contain minimal to no carbohydrates, focusing primarily on delivering a concentrated source of protein. This is achieved through careful selection of protein sources and processing methods.
Typical zero-carb protein powders primarily utilize protein isolates derived from sources like collagen and whey. Collagen, a structural protein found in connective tissues, is often favored for its purported joint health benefits and neutral taste. Whey protein isolate, a byproduct of cheese production, offers a higher protein concentration and faster digestion rate compared to other whey forms. Other sources, although less common in strictly “zero-carb” formulations, might include casein protein isolate (a slower-digesting milk protein).
While the term “zero-carb” is often used, it’s crucial to understand that trace amounts of carbohydrates might still be present due to processing or naturally occurring sugars. It’s vital to check the nutritional label for precise carbohydrate content.
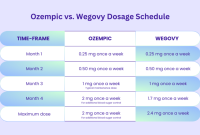
The following table compares the nutritional information (per serving) for three hypothetical popular brands of zero-carb protein powder. Actual values will vary depending on the specific product and serving size.
| Brand | Protein (grams) | Fat (grams) | Carbohydrates (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | 25 | 1 | <1 |
| Brand B | 30 | 2 | <1 |
| Brand C | 28 | 0.5 | 0 |
Weight Loss Mechanisms and Zero Carb Protein
Protein plays a crucial role in weight management through its impact on satiety and metabolic rate. High-protein diets can promote feelings of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake. Furthermore, protein requires more energy to digest than carbohydrates or fats, leading to a slight increase in metabolism.
A high-protein, zero-carb diet can be particularly effective for weight loss by prioritizing protein as the primary macronutrient. This approach minimizes insulin spikes associated with carbohydrate consumption, potentially promoting fat burning and preventing fat storage.
Below are examples of meal plans incorporating zero-carb protein powder. These are illustrative examples and should be adjusted based on individual caloric needs and activity levels.
- Meal Plan 1 (Higher Protein):
- Breakfast: Zero-carb protein shake (1 scoop) with unsweetened almond milk and MCT oil.
- Lunch: Large salad with grilled chicken or fish, avocado, and olive oil dressing.
- Dinner: Steak with steamed broccoli and a side of cauliflower mash.
- Meal Plan 2 (Moderate Protein):
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach and a side of bacon.
- Lunch: Leftover steak and broccoli from dinner.
- Dinner: Salmon with asparagus and a small portion of cheese.
- Snack: Zero-carb protein shake (½ scoop) with water.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
Beyond simple calorie reduction, zero-carb protein powder can offer several potential benefits. It may support muscle preservation during weight loss, improve satiety, and contribute to better blood sugar control in some individuals. However, consuming high amounts of protein has potential drawbacks.
Potential side effects of high-protein diets include digestive issues (constipation, bloating), increased risk of kidney stones (especially in individuals with pre-existing conditions), and potential strain on the kidneys. Long-term effects require further research, but maintaining adequate hydration and electrolyte balance is crucial to mitigate potential risks.
Compared to other weight loss strategies, a zero-carb, high-protein approach might yield quicker initial weight loss due to water loss and reduced carbohydrate storage. However, long-term sustainability and overall health outcomes depend on individual adherence and overall dietary balance.
Practical Application and Considerations

A workout routine complementing a zero-carb, high-protein diet should focus on strength training and moderate cardio. This approach helps maximize muscle retention and improve overall metabolic function.
- Strength training: 3 days per week, focusing on compound exercises (squats, deadlifts, bench press).
- Cardio: 2-3 days per week, 30-45 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise.
Incorporating zero-carb protein powder into different dietary lifestyles is straightforward. In ketogenic diets, it can be a convenient way to boost protein intake while keeping carbohydrates low. During intermittent fasting, it can be consumed during eating windows to support satiety and muscle protein synthesis.
Maintaining adequate hydration and electrolyte balance is crucial when following a zero-carb, high-protein diet. Increased protein intake can increase urine production, leading to electrolyte depletion. Consuming enough water and electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium) is vital for preventing adverse effects.
Recipes and Preparation Methods, Zero carb protein powder for weight loss

Here are three recipes incorporating zero-carb protein powder. These are examples and can be adapted to individual preferences.
- Recipe 1: Chocolate Peanut Butter Protein Shake
- Ingredients: 1 scoop zero-carb protein powder, 1 tbsp peanut butter, 1 cup unsweetened almond milk, ice cubes.
- Instructions: Blend all ingredients until smooth.
- Nutritional Information (Approximate): Protein: 25g, Fat: 15g, Carbs: <2g
- Recipe 2: Savory Protein Pancakes
- Ingredients: 1 scoop zero-carb protein powder, 2 eggs, 1 tbsp olive oil, salt and pepper to taste.
- Instructions: Whisk eggs, protein powder, olive oil, salt, and pepper. Cook on a lightly oiled pan like regular pancakes.
- Nutritional Information (Approximate): Protein: 20g, Fat: 10g, Carbs: <1g
- Recipe 3: Creamy Tomato Soup with Protein Boost
- Ingredients: 1 can crushed tomatoes, ½ cup bone broth, ½ scoop zero-carb protein powder, herbs (basil, oregano).
- Instructions: Simmer tomatoes and broth. Blend until smooth. Stir in protein powder and herbs.
- Nutritional Information (Approximate): Protein: 15g, Fat: 5g, Carbs: 5g
Tips and tricks for preparing palatable and nutritious zero-carb protein powder shakes and smoothies are detailed below.
| Tip | Description | Benefit | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use Cold Liquids | Mix powder with ice-cold water or milk. | Prevents clumping and creates a smoother texture. | Add ice to your blender. |
| Blend Thoroughly | Blend for at least 30 seconds to ensure the powder is fully dissolved. | Prevents gritty texture. | Use a high-powered blender. |
| Add Flavor Enhancers | Incorporate spices, extracts, or sweeteners. | Enhances taste and reduces blandness. | Add cocoa powder, vanilla extract, or a sugar-free sweetener. |
Zero-carb protein powder can be incorporated into savory dishes by adding it to sauces, soups, or meatloaf mixtures to increase protein content and create a richer texture.
Visual Representation of Information

A typical serving of zero-carb protein powder, depending on the source and brand, typically appears as a fine, slightly grainy powder. The color can range from off-white or light beige (collagen) to a slightly yellowish hue (whey isolate). The texture is generally smooth, although some brands may have a slightly coarser consistency.
Over time, a zero-carb, high-protein diet, coupled with consistent exercise, would ideally lead to a gradual decrease in body fat percentage and a corresponding increase in lean muscle mass. This would manifest as a more defined physique, with increased muscle tone and a reduction in overall body fat. The rate of these changes would vary depending on factors like individual metabolism, adherence to the diet, and exercise intensity.